bennettjc
Member
This data was first discussed here a year or so ago when it was released as a poster. It was now just published in a major urology journal.
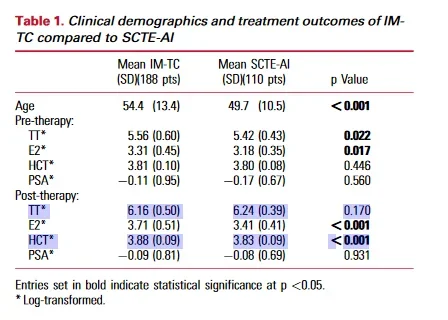
Bascially it suggested that 75 or 100mg of "Xyosted" (SubQ enanthate) each week leads to lower HCT/E2/PSA than does 100mg of IM cypionate.
This is a poor study. The two groups were not randomized (one group was lower) and some of the authors are on the Xyosted payroll.
I have the full paper if you are interested:

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Bascially it suggested that 75 or 100mg of "Xyosted" (SubQ enanthate) each week leads to lower HCT/E2/PSA than does 100mg of IM cypionate.
This is a poor study. The two groups were not randomized (one group was lower) and some of the authors are on the Xyosted payroll.
I have the full paper if you are interested:

Comparison of Outcomes for Hypogonadal Men Treated with Intramuscular Testosterone Cypionate versus Subcutaneous Testosterone Enanthate - PubMed
While IM-TC and SCTE-AI provide a significant increase in TT levels, SCTE-AI is associated with lower levels of post-therapy HCT and E2 compared to IM-TC after adjusting for significant covariates. SCTE-AI is an effective testosterone delivery system with a potentially preferable safety profile...