There is a lot of speculation that DHT causes benign prostatic hyperplasia, growth in the prostate. I see studies both for and against this, though I don't think it's definitive. However, reducing DHT is a treatment for BHP.
Also, high levels of DHT may cause reduced bone mass in your spine.
NOTE: I don't suggest dutasteride and finasteride, they seem to cause a lot of problems, BUT they are used to reduce DHT.
So I am not sure why high DHT is a good thing, I would't go out of my way to increase it.
What benefits does anyone expect from increasing DHT?
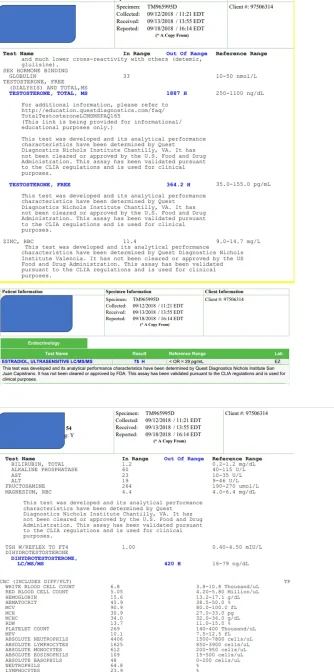
BTW, what is your PSA level? Is it higher than expected?
=================================================
5α-reductase inhibitors such as dutasteride and finasteride have been shown to modify the underlying pathology of symptomatic BPH, resulting in significant reductions in prostate volume and in the risks of AUR- and BPH-related surgery. They have also demonstrated improvements in urinary symptoms and flow.
The Clinical Benefits of Dutasteride Treatment for LUTS and BPH
============================================
Dihydrotestosterone May Not Affect Prostate Growth But May Reduce BMD
Compared with placebo, DHT reduced lumbar spine BMD (1.4%; 95% CI, 0.6% - 2.3%; P < .001) at 24 months but not hip BMD (P > .2) and increased serum aminoterminal propeptide of type I procollagen in the second year of the study. In the DHT group, levels of serum DHT and its metabolites were increased, whereas serum testosterone, estradiol, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone levels were suppressed. DHT increased hemoglobin levels (7%; 95% CI, 5% - 9%), serum creatinine levels (9%; 95% CI, 5% - 11%), and lean mass (2.4%; 95% CI, 1.6% - 3.1%) but reduced fat mass (5.2%; 95% CI, 2.6% - 7.7%; P < .001 for all).
We conclude that DHT acts as a hormone in tissues without high concentrations of 5α-reductase enzymes but mainly in an autocrine–paracrine manner in tissues like the prostate, in which 5α-reductase is abundant."
===========================================
The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. - PubMed - NCBI