We know that pregnenolone and progesterone increase allopregnanolone. Do you know any other hormones that increase allopregnanolone?

Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid derived from progesterone. It acts as a powerful positive allosteric modulator of GABA<sub>A</sub> receptors in the brain – in fact, it can enhance GABA’s inhibitory effect with potency far greater than benzodiazepinespmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Through this GABAergic action, allopregnanolone produces calming, anti-anxiety, and mood-stabilizing effects, earning it the nickname of a “natural tranquilizer” for the brain. Low allopregnanolone levels have been linked to mood disorders: studies find that patients with depression, anxiety, or PTSD often have significantly reduced allopregnanolone (for example, cerebrospinal fluid levels about half of normal in depressed patients)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Notably, successful treatment of these conditions – whether with antidepressants or other therapies – tends to raise allopregnanolone levels in parallel with mood improvementpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This highlights allopregnanolone’s importance in mental health and the potential benefit of boosting it.
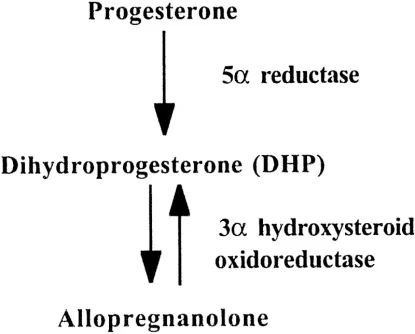
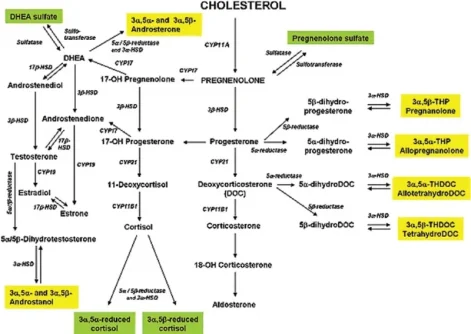
It’s important to understand how allopregnanolone is made. Like other steroid hormones, it ultimately originates from cholesterol: the body converts cholesterol to pregnenolone, then to progesterone, and finally into allopregnanolone via the 5α-reductase and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzymespmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Because allopregnanolone is a metabolite of progesterone, factors that affect progesterone levels or its metabolism will influence allopregnanolone productionrupahealth.com. This is particularly relevant for individuals on testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Exogenous testosterone can suppress upstream steroid hormones – TRT feedback lowers LH/FSH, leading to reduced testicular production of pregnenolone and progesterone (the precursors of allopregnanolone)excelmale.com. Some experts also suggest that long-term high-dose TRT may downregulate 5α-reductase activity, the enzyme needed to convert progesterone to allopregnanoloneexcelmale.com. In practice, men on TRT have been observed to have lower pregnenolone, progesterone, and slightly lower DHEA levelsexcelmale.com, which could translate to lower allopregnanolone and potentially impact mood or anxiety. Thus, finding ways to increase allopregnanolone is especially pertinent for someone on TRT to maintain neurosteroid balance.
Below is a comprehensive guide to strategies – natural and medical – for increasing allopregnanolone levels. These include dietary and lifestyle approaches, supplements, and medications, as well as special considerations for individuals on TRT. All recommendations are backed by scientific findings from peer-reviewed research or trusted clinical sources.
Diet can play a fundamental role in supporting the body’s neurosteroid synthesis. While no single “allopregnanolone-rich food” exists (since allopregnanolone is produced internally, not obtained directly from diet), eating a hormone-friendly diet provides the building blocks and favorable metabolic environment for allopregnanolone production:
Overall, a Mediterranean-style or whole-food diet is a good template: it provides plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats – thereby offering vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support the body’s hormone-producing machineryrupahealth.com. In short, feed your neuroendocrine system well so it has the substrates and co-factors to make allopregnanolone.
In addition to diet, certain supplements or specific nutrients can directly or indirectly boost allopregnanolone synthesis. These should ideally be used with guidance from a healthcare provider, especially when on TRT, but evidence suggests they may be helpful tools:
Summary of Supplement Strategies: The most targeted approach is to replenish the precursor hormones (pregnenolone, maybe progesterone, and DHEA) when they are low, since this directly feeds into making more allopregnanolone. This is often referred to as “upstreaming” the neurosteroid pathway. Clinical evidence supports that doing so can significantly elevate allopregnanolone levels and improve anxiety symptomsdiscountedlabs.comdiscountedlabs.com. Combining this with general nutrient support (vitamins, minerals) and possibly gentle herbal aids creates a strong foundation for neurosteroid balance. Always discuss with a doctor before starting these, especially on TRT, to tailor dosing and monitor hormone levels.
Several prescription treatments – including some groundbreaking new medications – work by boosting allopregnanolone or mimicking its effects. Additionally, certain existing drugs (used off-label) can influence allopregnanolone production:
In summary, the medical approaches to increase allopregnanolone or its activity range from indirect (SSRIs stimulating the body’s production) to direct (administering an ALLO analog like brexanolone/zuranolone). For someone on TRT looking to support mood and neurosteroid balance, a reasonable medical plan might be: ensure no concomitant medications are reducing allopregnanolone (see TRT section on finasteride), possibly use an SSRI if clinically indicated, and be aware of emerging neurosteroid treatments that could be options if needed. Always discuss risks and benefits with your physician; for example, adding an SSRI to TRT can help neurosteroids but might have sexual side effects – on the other hand, a low-dose SSRI might be enough to get a neurosteroid boost without significant side effectspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This kind of nuanced decision should be made collaboratively with a healthcare provider, weighing all factors.
Lifestyle habits can significantly influence one’s hormonal and neurochemical balance, including the levels of neurosteroids like allopregnanolone. By optimizing certain habits, you create a physiological environment conducive to higher allopregnanolone and better GABAergic tone. Here are key lifestyle strategies:
Implementing these lifestyle measures creates a supportive backdrop for any dietary, supplement, or medical interventions. Think of it as optimizing your internal ecosystem: less chronic stress hormones, better sleep, regular signals from exercise, and minimal toxin interference. This allows your body to produce the right amounts of neurosteroids when you need them. Many of these habits (stress reduction, exercise, sleep) have been individually shown to improve mood and anxiety on their own; by doing them, you’re likely elevating allopregnanolone and/or making your brain more responsive to it. Lifestyle changes often require consistency and may take weeks or months to fully reflect in hormone levels, but they form the foundation of long-term neuroendocrine health.
For individuals on TRT, there are additional factors to consider when trying to increase allopregnanolone:
In essence, for those on TRT, the strategy is to “backfill” what TRT suppresses. By doing so, you aim to enjoy the benefits of testosterone (energy, muscle, libido) and the benefits of adequate allopregnanolone (calm, mood resilience, reduced anxiety). Many TRT patients report the best outcomes when they address the whole hormone network rather than just testosterone alone. It may require a bit of trial and error with professional oversight, but it can lead to significantly improved quality of life.
Increasing allopregnanolone levels to support mental health is a multifaceted endeavor that involves nourishing your body, managing your stress and lifestyle, and possibly leveraging supplements or medications. Allopregnanolone is a potent neurosteroid “message carrier” of calm and balance in the brain, and as we’ve seen, it can be influenced through various routes:
For individuals on TRT, these strategies become even more pertinent – one must be proactive in maintaining the upstream hormone levels that TRT alone might diminishexcelmale.com. Integrating approaches like hCG therapy, periodic hormone monitoring, and judicious use of precursor supplements can make a significant difference in neurosteroid balance while on testosterone therapy.
It’s heartening to note that the role of allopregnanolone in mental health is gaining recognition in mainstream medicine. The success of treatments like brexanolone and zuranolone for depression showcases that modulating neurosteroids is a viable and effective therapeutic avenuefrontiersin.org. What this means for someone seeking to help themselves is that you are focusing on a truly impactful factor for mood and anxiety. By following the guide above, you are essentially implementing your own personalized “neurosteroid therapy” in a natural, holistic way.
Finally, always coordinate with healthcare professionals when making changes, especially in the context of TRT or if you have underlying health conditions. Hormones and neurosteroids form a complex web – adjusting one piece can affect others. A doctor can help order the right tests (to avoid guessing) and ensure that any supplementation or medication is done safely. That said, many of the lifestyle and dietary recommendations are safe and beneficial for overall health, so you can certainly start with those on your own. Improvements may be gradual, but over time you may notice steadier mood, less anxiety, better sleep, and an enhanced sense of well-being as your allopregnanolone levels build up or normalize.
In summary, boosting allopregnanolone is a promising strategy for supporting mental health. By fueling your brain’s ability to “make its own calm”, you address mood and anxiety at a fundamental level. It’s a comprehensive approach – part endocrine, part lifestyle – but the reward is potentially a more balanced mood from within. With persistence and careful management, you can harness the power of this neurosteroid to improve your quality of life, even while on therapies like TRT. Here’s to achieving a better neurohormonal balance and reaping the mental health benefits that come with it!
References:
Strategies to Increase Allopregnanolone for Mental Health Support
Introduction: Allopregnanolone, Mood, and TRT Context
Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid derived from progesterone. It acts as a powerful positive allosteric modulator of GABA<sub>A</sub> receptors in the brain – in fact, it can enhance GABA’s inhibitory effect with potency far greater than benzodiazepinespmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Through this GABAergic action, allopregnanolone produces calming, anti-anxiety, and mood-stabilizing effects, earning it the nickname of a “natural tranquilizer” for the brain. Low allopregnanolone levels have been linked to mood disorders: studies find that patients with depression, anxiety, or PTSD often have significantly reduced allopregnanolone (for example, cerebrospinal fluid levels about half of normal in depressed patients)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Notably, successful treatment of these conditions – whether with antidepressants or other therapies – tends to raise allopregnanolone levels in parallel with mood improvementpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This highlights allopregnanolone’s importance in mental health and the potential benefit of boosting it.
It’s important to understand how allopregnanolone is made. Like other steroid hormones, it ultimately originates from cholesterol: the body converts cholesterol to pregnenolone, then to progesterone, and finally into allopregnanolone via the 5α-reductase and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzymespmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Because allopregnanolone is a metabolite of progesterone, factors that affect progesterone levels or its metabolism will influence allopregnanolone productionrupahealth.com. This is particularly relevant for individuals on testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Exogenous testosterone can suppress upstream steroid hormones – TRT feedback lowers LH/FSH, leading to reduced testicular production of pregnenolone and progesterone (the precursors of allopregnanolone)excelmale.com. Some experts also suggest that long-term high-dose TRT may downregulate 5α-reductase activity, the enzyme needed to convert progesterone to allopregnanoloneexcelmale.com. In practice, men on TRT have been observed to have lower pregnenolone, progesterone, and slightly lower DHEA levelsexcelmale.com, which could translate to lower allopregnanolone and potentially impact mood or anxiety. Thus, finding ways to increase allopregnanolone is especially pertinent for someone on TRT to maintain neurosteroid balance.
Below is a comprehensive guide to strategies – natural and medical – for increasing allopregnanolone levels. These include dietary and lifestyle approaches, supplements, and medications, as well as special considerations for individuals on TRT. All recommendations are backed by scientific findings from peer-reviewed research or trusted clinical sources.
Dietary Strategies to Support Allopregnanolone Production
Diet can play a fundamental role in supporting the body’s neurosteroid synthesis. While no single “allopregnanolone-rich food” exists (since allopregnanolone is produced internally, not obtained directly from diet), eating a hormone-friendly diet provides the building blocks and favorable metabolic environment for allopregnanolone production:
- Include Healthy Fats and Cholesterol: Steroid hormones like progesterone and allopregnanolone are synthesized from cholesterol. Extremely low-fat or cholesterol-deficient diets may hinder optimal production of these hormones. Ensure the diet contains moderate amounts of healthy fats – for example, eggs (rich in cholesterol and choline), avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish. These foods supply cholesterol and essential fatty acids needed as precursors and support cell membranes in the brain where neurosteroids are synthesized. A balanced intake of omega-3 fatty acids (from fish like salmon, or flaxseed) is also beneficial; omega-3s help reduce neuroinflammation and have been linked to improved mood, potentially facilitating a better environment for neurosteroid activitypmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govsciencedirect.com. In fact, researchers suggest that diets rich in anti-inflammatory, PPAR-agonist nutrients (like omega-3s and polyphenols) may enhance the “PPAR–allopregnanolone axis,” promoting neurosteroidogenesis while reducing inflammationsciencedirect.com. (PPAR = peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, a nuclear receptor that when activated can increase neurosteroid production and decrease inflammation.)
- Ensure Sufficient Protein and Micronutrients: Adequate protein provides amino acids for overall neurotransmitter and hormone function (for example, taurine and glutamine support GABA production). But just as crucial are vitamins and minerals that serve as co-factors in steroid synthesis. A whole-food, nutrient-dense diet is recommendedrupahealth.com. Key nutrients include zinc, magnesium, and B-vitamins:
- Zinc is required for multiple enzyme functions in hormone production and is known to support progesterone and testosterone synthesis. Foods high in zinc (oysters, shellfish, beef, pumpkin seeds) can be helpful.
- Magnesium participates in over 300 biochemical reactions, including those in the nervous system; it supports GABAergic signaling and may indirectly aid neurosteroid function. Green leafy vegetables, nuts, and whole grains provide magnesium.
- Vitamins B5 and B6 are important for steroid hormone production and neural health – vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is a component of CoA, needed for converting cholesterol to pregnenolone, and B6 (pyridoxine) helps in neurotransmitter synthesis (including GABA) and may support the progesterone → allopregnanolone pathway. These are found in poultry, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Vitamin C is highly concentrated in the adrenal glands (where pregnenolone and other steroids are made) and is involved in adrenal steroidogenesis; citrus fruits, berries, and peppers can supply ample vitamin C.
- Phytonutrients and Herbal Foods: Certain plant compounds might encourage neurosteroid balance. For instance, flavonoids and polyphenols (found in colorful fruits, vegetables, green tea, cocoa) can modulate brain inflammation and oxidative stress, indirectly supporting healthy neurosteroid levels. Curcumin (from turmeric) and resveratrol (from grapes/red wine) are examples of polyphenols that activate pathways (like PPAR-gamma) linked to improved mood and neurogenesispmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. While research is ongoing, consuming a variety of plant foods as part of a balanced diet is thought to be beneficial for hormone equilibrium.
- Balanced Meals for Blood Sugar Control: Keeping blood sugar stable through a balance of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates each meal can prevent excessive stress hormone spikes. Large swings in blood glucose/insulin can provoke cortisol release, which might divert more pregnenolone toward cortisol production at the expense of progesterone/allopregnanolone (sometimes referred to as the “pregnenolone steal”). Thus, emphasize low-glycemic carbs (like whole grains, vegetables, legumes) and avoid high sugar binges to reduce unnecessary adrenal stress.
Overall, a Mediterranean-style or whole-food diet is a good template: it provides plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats – thereby offering vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support the body’s hormone-producing machineryrupahealth.com. In short, feed your neuroendocrine system well so it has the substrates and co-factors to make allopregnanolone.
Key Supplements and Nutrients Influencing Neurosteroid Levels
In addition to diet, certain supplements or specific nutrients can directly or indirectly boost allopregnanolone synthesis. These should ideally be used with guidance from a healthcare provider, especially when on TRT, but evidence suggests they may be helpful tools:
- Pregnenolone: Pregnenolone is the master precursor steroid hormone – often dubbed the “mother hormone” – from which progesterone, DHEA, and others are made. Supplementing pregnenolone can increase the availability of substrate to ultimately convert into allopregnanolone. In fact, clinical studies have shown a dramatic rise in allopregnanolone levels after pregnenolone administration. For example, a single high dose of 400 mg oral pregnenolone tripled serum allopregnanolone levels within about 2 hoursdiscountedlabs.com. Another trial in patients with mood disorders used a regimen up to 500 mg/day of pregnenolone; results showed allopregnanolone levels increased roughly five-fold, along with significant increases in progesterone (4×) and pregnenolone sulfate (3×)discountedlabs.com. These findings confirm that pregnenolone is indeed converted downstream into neuroactive steroids like allopregnanolone in humans. Most over-the-counter pregnenolone supplements come in much lower doses (10–50 mg); such doses may have more subtle effects, but even moderate doses have been observed to raise pregnenolone and allopregnanolone levels somewhat over baselinediscountedlabs.com. Users often report improvements in mood, stress tolerance, and mental clarity with pregnenolone – likely due to its conversion to allopregnanolone and related neurosteroids supporting GABA and NMDA receptors. Caution: High-dose pregnenolone should be medically supervised; possible side effects include irritability or insomnia in some (especially if too much converts to cortisol). Starting low (e.g. 10–30 mg) and titrating up is a prudent approach, checking hormone levels periodically.
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone): DHEA is another adrenal steroid that, while not on the direct pathway to allopregnanolone, plays a role in the broader neurosteroid milieu. DHEA can convert into androgens and estrogens, relieving some demand on progesterone for those pathways. In men on TRT, endogenous DHEA production might drop slightlyexcelmale.com, so supplementation can restore physiological levels. Maintaining DHEA in the normal range could indirectly support neurosteroid balance (and DHEA itself has some neuroactive properties and mild GABA-antagonistic metabolite DHEA-S, which complement allopregnanolone’s GABA-agonism for a healthy balance). Clinical trials have found DHEA supplementation improves mood and energy in individuals with depression or adrenal insufficiency. A common dose is 25–50 mg/day for men (lower for women), but it should be individualized and monitored via blood tests to avoid excess. While DHEA may not directly raise allopregnanolone, it is part of the same hormonal network and can support overall mental well-being and hormone balance – making it a useful adjunct if tests show low DHEA-S levels.
- Bioidentical Progesterone: Progesterone is the direct precursor to allopregnanolone, so providing extra progesterone can acutely raise allopregnanolone production. In women, supporting adequate progesterone during the luteal phase (through diet, stress management, or in some cases progesterone supplementation) is known to increase allopregnanolone and help with symptoms of PMS or PMDDpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. For instance, luteal-phase progesterone levels correlate with allopregnanolone levels; when progesterone rises (such as during pregnancy), allopregnanolone concurrently rises to high levels, whereas a sudden progesterone drop postpartum causes a steep fall in allopregnanolone, potentially triggering mood issuesrupahealth.comrupahealth.com. Supplementing progesterone (e.g. oral micronized progesterone, 50–200 mg at night, or transdermal cream) is a well-established treatment in women for luteal support, menopausal symptoms, and postpartum mood in some cases – part of its calming, sedative effect is attributed to its metabolism into allopregnanolone in the brainpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Interestingly, progesterone’s anxiolytic effects are observed in men as well: studies administering progesterone to male volunteers found sedative and anti-anxiety outcomes, likely mediated by conversion to allopregnanolonepmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. In one study, progesterone injections (50–100 mg) in men blunted stress-related negative mood and facilitated emotional recovery, consistent with allopregnanolone’s stress-buffering rolepmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Therefore, some clinicians have experimented with low-dose progesterone in men on TRT who have anxiety or sleep disturbances. Typically, a very low dose (5–10 mg of oral or cream progesterone at bedtime) might be used to avoid excessive feminizing effects while providing a neurosteroid boost. Note: Men should only do this under medical guidance, as too much progesterone can cause side effects (fatigue, low libido). But when properly balanced, a little progesterone can significantly increase brain allopregnanolone – promoting relaxation and sleep.
- Vitamins and Antioxidants: While not “neurosteroids” themselves, certain vitamins can enhance neurosteroidogenesis:
- Vitamin D: Actually a seco-steroid hormone, vitamin D has been shown to modulate brain chemicals and inflammation. Deficiency in vitamin D is associated with depression. Ensuring sufficient vitamin D (through sunlight or supplements if needed) might indirectly facilitate a healthy hormonal environment.
- Vitamin C and E: As antioxidants, they protect steroid-producing glands from oxidative stress. Vitamin C, as mentioned, is needed for adrenal steroid output; vitamin E (found in nuts, seeds) helps stabilize cell membranes (including myelinated nerve cells where neurosteroids act). Together, they may support the integrity of neurosteroid pathways.
- Herbal and Botanical Supplements: A few herbs are notable for their hormone-modulating effects:
- Chaste Tree Berry (Vitex agnus-castus): Vitex is well known to gently raise luteinizing hormone and promote progesterone production in females. It’s often used to alleviate PMS/PMDD symptoms. By supporting a higher natural progesterone level, Vitex may lead to more allopregnanolone formation as a downstream effectrupahealth.com. Some women taking Vitex report reduced anxiety and improved mood in the luteal phase, which could be due to that neurosteroid increase. (Vitex is usually not used in men, as it can lower male libido by reducing androgens, but in women it’s a popular remedy for luteal phase issues.)
- Adaptogens (Ashwagandha, Rhodiola, etc.): Adaptogenic herbs help normalize the stress response. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera), for example, has been shown to reduce chronically elevated cortisol and may modestly influence DHEA levelspubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. By lowering cortisol, these herbs potentially free more pregnenolone to be available for sex hormone and neurosteroid synthesis rather than being shunted into making cortisol. They also may upregulate GABA receptors or calming neurotransmitters. Many users of ashwagandha report decreased anxiety and better sleep – effects that could complement allopregnanolone’s function. While direct studies on adaptogens increasing allopregnanolone are lacking, their overall impact on stress hormone balance makes them a worthy consideration.
- Licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra): Licorice can prolong the half-life of cortisol (by inhibiting its breakdown) and has complex effects on hormone metabolism. In moderate doses, licorice might actually lower testosterone but raise progesterone levels (as seen in some polycystic ovary syndrome studies). However, its role in neurosteroids isn’t clear, so it’s not a primary recommendation here – and chronic use can cause side effects (high blood pressure, etc.).
- Others: Some nutritional supplements like phosphatidylserine, L-theanine, and magnesium glycinate are known to improve sleep quality and stress resilience, potentially supporting neurosteroid function indirectly. Magnesium in particular, as mentioned, is a co-factor and also a natural anxiolytic that can synergize with GABA (it’s often given at night to help calm the nervous system). While these don’t raise allopregnanolone per se, they are supportive measures for overall GABAergic tone.
Summary of Supplement Strategies: The most targeted approach is to replenish the precursor hormones (pregnenolone, maybe progesterone, and DHEA) when they are low, since this directly feeds into making more allopregnanolone. This is often referred to as “upstreaming” the neurosteroid pathway. Clinical evidence supports that doing so can significantly elevate allopregnanolone levels and improve anxiety symptomsdiscountedlabs.comdiscountedlabs.com. Combining this with general nutrient support (vitamins, minerals) and possibly gentle herbal aids creates a strong foundation for neurosteroid balance. Always discuss with a doctor before starting these, especially on TRT, to tailor dosing and monitor hormone levels.
Medications and Medical Therapies that Elevate Allopregnanolone
Several prescription treatments – including some groundbreaking new medications – work by boosting allopregnanolone or mimicking its effects. Additionally, certain existing drugs (used off-label) can influence allopregnanolone production:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): It may come as a surprise, but beyond their effects on serotonin, SSRIs have a unique property: at low doses, SSRIs can act as “Selective Brain Steroidogenic Stimulants.” Research led by Pinna and colleagues discovered that SSRIs like fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline, paroxetine, and fluvoxamine markedly increase brain allopregnanolone levels by enhancing the activity of the enzymes that synthesize this neurosteroidpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This effect seems to be independent of their serotonin reuptake inhibition – it occurs even at doses below those needed to affect serotonin. For instance, experiments showed that sub-micromolar concentrations of S-norfluoxetine (an active metabolite of fluoxetine) – too low to alter serotonin – selectively increased brain allopregnanolone content and abolished aggression in micepmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. In humans, depressed patients treated with fluoxetine or fluvoxamine had their CSF allopregnanolone levels normalize (rise to healthy levels), and the degree of ALLO increase correlated with improvement in depression and anxiety symptomspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This has led to the idea that SSRIs’ therapeutic effects might be partly due to restoring neurosteroid balance. From a practical standpoint, an SSRI could be considered (in consultation with a psychiatrist) if someone has persistent anxiety or depression possibly linked to low allopregnanolone – even if their primary goal is neurosteroid enhancement. Off-label usage: Some researchers have proposed ultra-low-dose SSRIs just for the allopregnanolone boost without full serotonergic action, but this isn’t a standard practice yet. Nevertheless, for individuals who have both mood symptoms and signs of low neurosteroid levels, an SSRI at a typical antidepressant dose may serve dual purpose. (Do note, SSRIs themselves can have side effects, and in men they can sometimes dampen sexual function/libido – something to weigh, especially if the person is on TRT to improve well-being. The decision should be personalized.)
- Brexanolone (Zulresso): Brexanolone is essentially pharmaceutical allopregnanolone. It’s a form of allopregnanolone administered as an IV infusion and was the first medication approved specifically for postpartum depression in 2019frontiersin.org. During the 60-hour infusion of brexanolone, patients receive a dose that restores their allopregnanolone to high normal levels, leading to rapid relief of severe depression in many cases. The treatment’s success underscores how powerful this neurosteroid is in lifting mood. However, brexanolone requires hospital supervision (due to risks like excessive sedation or fainting during infusion) and is extremely costly; thus it’s reserved for extreme cases (e.g. postpartum depression with psychosis). It’s not a practical everyday treatment for general anxiety or for someone on TRT – but it validates allopregnanolone as a therapeutic target. Knowing that brexanolone exists reinforces the value of trying to raise one’s own allopregnanolone through the more accessible means we’re discussing.
- Zuranolone (Zurzuvae): This is a new oral neurosteroid-based antidepressant that was approved by the FDA in 2023 for postpartum depressionfrontiersin.org (and under investigation for major depressive disorder). Zuranolone is an analog of allopregnanolone designed to be taken as a pill (over a 2-week course) to produce similar GABA-boosting effects. In clinical trials, zuranolone has shown rapid antidepressant and anti-anxiety effects, presumably by activating GABA receptors in the same way allopregnanolone doesfrontiersin.orgfrontiersin.org. The availability of zuranolone means that in the near future, doctors could prescribe a neurosteroid modulator directly for mood support outside of the postpartum context as well. It’s a shorter-term, on-off treatment (not a daily forever pill like SSRIs), which is an interesting new paradigm. For the user asking this question, it’s useful to know that such medications exist – while you focus on natural strategies, you can follow the development of drugs like zuranolone, as they might become options for treating chronic anxiety or depression by pharmacologically raising neurosteroid activity.
- Benzodiazepines and Related GABAergic Drugs: Traditional anti-anxiety medications like benzodiazepines (e.g. lorazepam, alprazolam) or non-benzo hypnotics (zolpidem/Ambien) do not increase allopregnanolone levels, but they simulate some of its effects by binding to GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor sites. They can provide short-term relief for anxiety or insomnia by enhancing GABA signaling. However, they come with issues of tolerance, dependence, and they don’t address the underlying neurosteroid deficiency. In fact, chronic use can actually alter GABA receptor subunits in a way that might reduce the efficacy of allopregnanolone over timerupahealth.com. Thus, while benzodiazepines can be a crutch for acute anxiety, they are not a strategy for raising allopregnanolone (and in some cases, long-term use could be counterproductive). A better medical approach to mimic allopregnanolone is using the neurosteroid analogs (like the ones above) or promoting natural production via SSRIs or hormone precursors.
- Other Prescription Options (Off-Label):
- Ketamine/Esketamine: The rapid-acting antidepressants ketamine and esketamine work via NMDA receptor antagonism primarily, but there’s some evidence they might interact with the glutamate/GABA balance and possibly downstream neurosteroids (ketamine has been noted to acutely increase pregnenolone and progesterone in animal models). While not a direct ALLO-boosting strategy, ketamine’s profound effects on reducing depression and possibly resetting stress responses could indirectly help normalize neurosteroid levels after relief of chronic stress. This is speculative but worth noting as part of the psychiatric toolkit.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): Interestingly, older antidepressants like imipramine or amitriptyline do not show the same robust allopregnanolone increase as SSRIsresearchgate.net, so they are not particularly useful for this purpose. The neurosteroid elevation seems unique to SSRIs among antidepressants.
- Atypical Antipsychotics: Some evidence (e.g. studies with fluoxetine + olanzapine in rats) suggested combined therapy can raise allopregnanolone more than either alonejournals.sagepub.com. This is more relevant in research settings or severe cases (like psychotic depression); atypical antipsychotics are generally not used just to raise ALLO due to their side effect profile, but if a patient is on one, it might be influencing their neurosteroids too.
- Ganaxolone: Ganaxolone is an investigational drug (an analog of allopregnanolone modified to avoid metabolism) that has been studied in epilepsy and rare neurodevelopmental disorders. It essentially acts like allopregnanolone at GABA receptors and has anti-seizure and anti-anxiety properties. It’s not yet widely available for general use, but it’s another example of a therapy aimed at leveraging allopregnanolone’s mechanism. If approved, it might see use in refractory anxiety or PTSD in the future.
In summary, the medical approaches to increase allopregnanolone or its activity range from indirect (SSRIs stimulating the body’s production) to direct (administering an ALLO analog like brexanolone/zuranolone). For someone on TRT looking to support mood and neurosteroid balance, a reasonable medical plan might be: ensure no concomitant medications are reducing allopregnanolone (see TRT section on finasteride), possibly use an SSRI if clinically indicated, and be aware of emerging neurosteroid treatments that could be options if needed. Always discuss risks and benefits with your physician; for example, adding an SSRI to TRT can help neurosteroids but might have sexual side effects – on the other hand, a low-dose SSRI might be enough to get a neurosteroid boost without significant side effectspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This kind of nuanced decision should be made collaboratively with a healthcare provider, weighing all factors.
Lifestyle Factors that Modulate Neurosteroid Balance
Lifestyle habits can significantly influence one’s hormonal and neurochemical balance, including the levels of neurosteroids like allopregnanolone. By optimizing certain habits, you create a physiological environment conducive to higher allopregnanolone and better GABAergic tone. Here are key lifestyle strategies:
- Stress Management: Chronic stress is an enemy of hormonal balance. When you are under prolonged stress, your body pumps out cortisol from the adrenal glands. High cortisol not only can contribute to anxiety itself, but it also can divert pregnenolone away from sex hormones and neurosteroids – a concept sometimes called the pregnenolone steal. In a high-cortisol state, the body might produce less progesterone (since pregnenolone is being used to make cortisol), thus lowering the substrate for allopregnanolone. Moreover, studies in stress-related disorders (like PTSD) have found a “block” in allopregnanolone synthesis — likely due to changes in enzyme expression under chronic stresspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Actively managing stress can mitigate these effects. Techniques such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, yoga, tai chi, or mindfulness practices have been shown to reduce cortisol levels and balance the HPA (hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal) axisrupahealth.com. Even simple habits like taking short relaxation breaks, walking in nature, or engaging in hobbies can lower perceived stress. Over time, reducing chronic stress will promote higher sex hormone production and facilitate progesterone’s conversion to allopregnanolone rather than to cortisolrupahealth.com. Think of it as allowing your body to allocate resources to “thriving” functions (like neurosteroid synthesis) instead of “surviving” functions (fight-or-flight chemistry).
- Healthy Sleep Patterns: Sleep and neuroendocrine health are deeply intertwined. The majority of restorative hormone release (growth hormone, testosterone, etc.) occurs during deep sleep. Poor sleep or insomnia can disrupt this hormonal pulsatility and is associated with reduced levels of various neuroactive steroids. For example, inadequate sleep can raise cortisol and lower anabolic hormones, indirectly impairing progesterone/allopregnanolone pathwaysrupahealth.com. In women, sleep disturbances have been linked to menstrual cycle hormone irregularitiesrupahealth.com, and in both sexes, chronic insomnia often coincides with anxiety and mood issues (which could be both cause and effect of low allopregnanolone). Prioritize 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night. Maintain good sleep hygiene: consistent sleep-wake times, a dark cool bedroom, limiting screens and bright light in the evening, and avoiding caffeine late in the day. If you suspect you have a sleep disorder (like sleep apnea), seek treatment, as resolving it can dramatically improve hormone regulation. By getting sufficient quality sleep, you support your brain’s natural neurosteroid rhythm – research indicates this can optimize reproductive hormone levels and by extension neurosteroid levelsrupahealth.com. Tip: Taking oral micronized progesterone at night (for those who are supplementing it) can aid sleep because of allopregnanolone’s soporific effect; this is often prescribed in menopausal women for insomnia.
- Regular Exercise (in Moderation): Exercise is a bit of a “Goldilocks” factor for neurosteroids – just the right amount confers benefits, while extreme overtraining could be counterproductive. Moderate, regular exercise has been shown to reduce anxiety and improve mood, and animal studies suggest one mechanism may be via increasing neurosteroid levels. In an interesting rodent study, mild exercise (low-intensity treadmill running) in older rats actually elevated brain allopregnanolone levels, and this increase was linked to the exercise’s pain-relieving and anti-anxiety effect (when researchers blocked allopregnanolone synthesis with a 5α-reductase inhibitor, the benefits of exercise were lost)pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This implies that part of the reason exercise makes us feel good is a boost in neurosteroids like allopregnanolone. For humans, adopting a routine of aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, combined with some resistance training (weights or bodyweight exercises), a few times a week is ideal. These activities help regulate stress hormones, improve metabolic health (which influences hormone production), and can even directly stimulate the brain (BDNF release, etc.) promoting resilience. However, avoid chronic overtraining or lack of recovery, as that can elevate cortisol continuously and potentially suppress sex hormones. The goal is regular moderate exercise, not pushing to absolute exhaustion. Even practices like yoga are doubly beneficial – giving both physical exercise and stress reduction, and yoga in particular has been found to increase GABA levels in the brain in some studies. Over time, an active lifestyle will contribute to maintaining a healthy balance of neurosteroids, while a sedentary lifestyle can worsen hormonal stagnation.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: These are two common substances that affect GABA and neurosteroids. Alcohol in the short term can increase allopregnanolone – this surge is thought to contribute to alcohol’s relaxing and disinhibitory effects (sometimes called “chemical courage”) because alcohol induces the adrenal glands and brain to convert more progesterone to allopregnanolone. However, the relationship is complex: chronic heavy alcohol use will dysregulate your neurosteroid system, potentially leading to tolerance (diminished GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor response) and a crash in allopregnanolone during withdrawalrupahealth.com. In fact, abrupt cessation in alcohol-dependent individuals can cause a rebound anxiety partly because allopregnanolone levels drop. The bottom line: moderation is key. If you drink, keep it light-to-moderate (e.g. a glass of wine with dinner) and avoid habitual heavy drinking. Excessive alcohol also harms sleep quality and liver metabolism of hormones. The Rupa Health summary advises moderating alcohol to protect hormone balancerupahealth.com. As for caffeine, it doesn’t directly impact allopregnanolone synthesis, but high doses can increase anxiety and cortisol in some people, which isn’t helpful for the calm neurosteroid tone you’re aiming for. A cup or two of coffee or tea is fine for most, but avoid jitter-inducing amounts and don’t use caffeine as a substitute for addressing fatigue (or it can become a stress on the system).
- Avoid Endocrine Disruptors: Modern life exposes us to various chemicals that can interfere with our hormones. Some of these, known as endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs), can mimic or block hormone receptors or alter hormone metabolism. For example, compounds in certain plastics (like BPA), phthalates in personal care products, some pesticides, and even phytoestrogens in large amounts can skew the delicate hormonal milieurupahealth.com. While research on EDCs has focused more on reproductive and thyroid hormones, anything that perturbs overall hormone balance could indirectly affect neurosteroids as well (since they share common pathways). To be safe, try to minimize exposure: use glass or stainless steel instead of plastic for food storage when possible, choose natural or phthalate-free personal care items, filter drinking water if in an area with contaminants, and opt for organic foods to reduce pesticide ingestion. This reduces the “background noise” of endocrine disruption, letting your body’s own hormone signals operate more cleanly.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Both underweight and overweight extremes can impact hormone levels. Significantly low body fat (as seen in some athletes or in anorexia) can lead to low cholesterol intake/storage and impaired gonadal hormone production – which would obviously reduce progesterone and allopregnanolone. On the other hand, being overweight, especially with high visceral fat, can create high aromatase activity (converting more testosterone into estrogen) and insulin resistance, which can suppress SHBG and alter the balance of free hormones. Obesity in women is sometimes linked to lower allopregnanolone in certain phasesec.bioscientifica.com and in men, metabolic syndrome can lower testosterone and DHEA, indirectly affecting neurosteroids. The advice is to aim for a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exerciserupahealth.com. If on TRT, this is often already part of the plan (since TRT can aid in fat loss and muscle gain when combined with exercise). Avoid crash diets or extreme bulking cuts, as those yo-yo effects stress the endocrine system. Instead, steady sustainable habits keep hormones (and neurosteroids) stable.
- Social Support and Mental Wellness Practices: While harder to quantify, having strong social connections, engaging in meaningful activities, and practices like therapy or journaling can reduce stress and improve mental resilience. Lower baseline anxiety and depression through such means may correlate with more normalized neurosteroid levels. There’s evidence that psychotherapy can alter brain chemistry; for instance, cognitive-behavioral therapy in PTSD not only reduces symptoms but has been associated with normalization of stress hormone profiles. So taking care of mental health through non-pharmacological means can synergize with the physiological strategies.
Implementing these lifestyle measures creates a supportive backdrop for any dietary, supplement, or medical interventions. Think of it as optimizing your internal ecosystem: less chronic stress hormones, better sleep, regular signals from exercise, and minimal toxin interference. This allows your body to produce the right amounts of neurosteroids when you need them. Many of these habits (stress reduction, exercise, sleep) have been individually shown to improve mood and anxiety on their own; by doing them, you’re likely elevating allopregnanolone and/or making your brain more responsive to it. Lifestyle changes often require consistency and may take weeks or months to fully reflect in hormone levels, but they form the foundation of long-term neuroendocrine health.
Special Considerations for Those on Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
For individuals on TRT, there are additional factors to consider when trying to increase allopregnanolone:
- Understand TRT’s Impact on “Upstream” Hormones: As noted earlier, TRT can suppress the body’s natural production of certain hormones. When you take exogenous testosterone, your pituitary gland reduces LH (luteinizing hormone) secretion. In men, LH normally stimulates the testes not only to produce testosterone but also to produce pregnenolone and progesterone (as intermediate steps in steroidogenesis). With low LH, testicular output of pregnenolone/progesterone drops, and the adrenal glands may not fully compensateexcelmale.com. Over time, men on TRT might have plenty of testosterone and DHT, but unusually low levels of pregnenolone, progesterone, and even DHEA compared to pre-TRT or age-matched non-TRT menexcelmale.com. This scenario can contribute to symptoms like anxiety or reduced stress tolerance in some, because you’ve effectively “pinched off” the neurosteroid supply line that comes from those precursors. Some clinicians believe this is one reason a subset of men on TRT report persistent anxiety or brain fog despite optimal T levels – their neurosteroid (allopregnanolone) levels may be lagging. Furthermore, Dr. Mark Gordon and others in the neurosteroid research field have postulated that high levels of exogenous testosterone can saturate or downregulate 5α-reductase, the enzyme that’s also needed to convert progesterone to allopregnanoloneexcelmale.com. The idea is that if 5α-reductase is heavily used to convert T→DHT, its activity or availability for converting progesterone might diminish (“burn out” over years of TRT), leading to lower allopregnanolone. While more research is needed to fully confirm this mechanism, it’s a consideration.
- Monitoring and Lab Work: If you are on TRT and concerned about neurosteroid levels, talk to your doctor about checking pregnenolone, progesterone, and DHEA(-S) levels in your blood. These are not always part of routine TRT monitoring, but they can be measured by most labs. If you find, for example, that your pregnenolone or progesterone is indeed very low (which is common on TRTexcelmale.com), that provides a rationale to intervene. Some hormone specialists offer comprehensive hormone panels for TRT patients that include these upstream hormonesexcelmale.com. Knowing your baseline can help target supplementation (e.g., if DHEA-S is low, use DHEA; if pregnenolone is low, consider pregnenolone supplement, etc.). It’s generally a good idea to do this under the guidance of an endocrinologist or a hormone replacement specialist.
- Consider hCG “Add-Back”: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) is an LH analog often used in TRT protocols to maintain fertility and testicular size. But it may have another benefit: hCG can stimulate the testes to produce progesterone and related neurosteroids in addition to testosterone. In women, hCG in the luteal phase dramatically increases progesterone and allopregnanolone from the ovariespubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. In men, hCG therapy has been noted to raise 17-OH progesterone and pregnanolone levels significantlyexcelmale.com, which suggests it’s activating those steroid pathways. A study on isolated human testes cells showed that hCG can induce production of not just testosterone but also other steroids in the pathway (though data on allopregnanolone specifically in men is limited, we extrapolate from the female corpus luteum study)pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Many TRT practitioners prescribe 500–1500 IU of hCG two or three times per week alongside testosterone. Subjectively, some men report feeling calmer and an improved sense of well-being when hCG is included – possibly because it’s helping restore some of the pregnenolone → progesterone → allopregnanolone conversion that was suppressed. If you are on TRT and not currently using hCG, it’s worth discussing with your provider, especially if maintaining fertility or neurosteroid production is a goal. (Be aware, though, that adding hCG might raise estrogen a bit too, since more testosterone is made internally, so anastrozole or other adjustments might be needed – it’s a balancing act.)
- Supplement Upstream Hormones if Needed: Depending on lab results and symptoms, supplementation with pregnenolone or DHEA while on TRT can be quite beneficial. As detailed earlier, pregnenolone can directly feed allopregnanolone synthesis. Some doctors start men on TRT with a low dose pregnenolone (e.g. 25 mg daily in the morning) and DHEA (25 mg daily) to “complete the pathway.” This is somewhat empirical, but anecdotal reports and small studies indicate it can improve mood, memory, and reduce the “anxiety gap” that TRT alone might not fill. One pilot study in men with traumatic brain injury (where neurosteroids are often low) used pregnenolone to successfully improve mood and cognitiondiscountedlabs.com. Again, ensure you are working with a knowledgeable provider for dosing and monitoring. Over-the-counter pregnenolone and DHEA are available, but one should confirm quality and dose accuracy (compounded pharmacies can also make prescriptions for these in desired doses). The goal is to approximate a more natural physiologic milieu: TRT gives you youthful T levels, and pregnenolone/DHEA give back some of the youthful neurosteroid milieu.
- Cautious Use of Progesterone in Men: Progesterone supplementation is not commonly done in men, but some anti-aging physicians do prescribe a very low dose progesterone cream (like 5 mg) at night for men who have insomnia or anxiety on TRT. The rationale is to directly produce a pulse of allopregnanolone in the brain during the night, helping sleep and calmness. Male bodies are quite sensitive to progesterone (since they usually have low levels), so only a tiny amount is needed. If a man on TRT has tried everything (pregnenolone, DHEA, etc.) and still has issues with anxiety or poor sleep, a trial of low-dose progesterone might be considered. Clinical literature on this is sparse, so it’s experimental. If pursued, it should be monitored (excess progesterone in men can cause side effects like lethargy or gynecomastia over time). But recall the study mentioned earlier: men injected with 100 mg progesterone showed reduced stress reactions and faster emotional recovery, presumably via neurosteroid effectspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. This suggests that, in acute situations, raising progesterone/allopregnanolone even in males can be beneficial. The key is finding a balance that helps and doesn’t overshoot.
- Avoid 5α-Reductase Inhibitors (Finasteride/Dutasteride) if Possible: Many men on TRT consider medications like finasteride to prevent testosterone’s conversion to DHT (for hair loss or prostate concerns). It’s crucial to recognize that finasteride will also inhibit the 5α-reductase conversion of progesterone to 5α-dihydroprogesterone, the precursor of allopregnanolone. In other words, finasteride can significantly lower allopregnanolone synthesis. This is strongly suspected to be a mechanism behind post-finasteride syndrome, where men experience depression, anxiety, and cognitive problems after using finasteride. Research confirms that finasteride and similar drugs reduce allopregnanolone levels and can alter GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor expression, often leading to mood side effectsrupahealth.com. If your goal is to maximize allopregnanolone, steer clear of 5α-reductase inhibitors. For hair preservation, you might explore alternatives: topical minoxidil, low-level laser therapy, or even low-dose topical finasteride (to limit systemic absorption) – though caution is still advised. Some newer hair loss treatments (like RU58841 or stem cell therapies) are being studied that might not affect 5α-reductase. For prostate health, natural interventions (saw palmetto, rye pollen extract) could be options, but note that saw palmetto also has some 5α-R blocking activity (though weaker). Always inform your doctor that you prioritize neurosteroid health; a good provider will help find a balance between different health goals.
- Be Mindful of Other Med Interactions: Certain medications (beyond finasteride) can impact neurosteroids. For instance, some anticonvulsants and steroids (like high-dose corticosteroids) can lower allopregnanolone. If you require such medications, discuss mitigation strategies with your doctor. Conversely, if you are using any sedatives or GABA-acting drugs, remember they might mask an allopregnanolone deficit or change receptor sensitivity. The strategy of increasing allopregnanolone might allow you to reduce reliance on some anxiolytic medications over time (with medical guidance).
In essence, for those on TRT, the strategy is to “backfill” what TRT suppresses. By doing so, you aim to enjoy the benefits of testosterone (energy, muscle, libido) and the benefits of adequate allopregnanolone (calm, mood resilience, reduced anxiety). Many TRT patients report the best outcomes when they address the whole hormone network rather than just testosterone alone. It may require a bit of trial and error with professional oversight, but it can lead to significantly improved quality of life.
Conclusion
Increasing allopregnanolone levels to support mental health is a multifaceted endeavor that involves nourishing your body, managing your stress and lifestyle, and possibly leveraging supplements or medications. Allopregnanolone is a potent neurosteroid “message carrier” of calm and balance in the brain, and as we’ve seen, it can be influenced through various routes:
- Nutritionally: by eating a balanced diet with adequate healthy fats, essential nutrients, and anti-inflammatory foods to provide the raw materials for neurosteroid synthesisrupahealth.comsciencedirect.com.
- Supplementally: by restoring key precursors like pregnenolone and DHEA (especially important if they’re low on labs) to directly boost allopregnanolone productiondiscountedlabs.com. Also, by considering herbal supports that encourage progesterone production (such as chasteberry) or reduce cortisol (like ashwagandha)rupahealth.comrupahealth.com, we can tilt the balance toward greater allopregnanolone output.
- Medically: via certain prescriptions known to raise neurosteroid levels – notably SSRIs in low-to-moderate doses which have been shown to upregulate allopregnanolone in the brainpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, or newer neurosteroid analog medications for depression that act on the same pathways. We also emphasize avoiding medications that impede allopregnanolone (such as finasteride) due to their documented negative impact on moodrupahealth.com.
- Lifestyle-wise: through stress reduction, good sleep, and exercise, which collectively lower the “brakes” (like cortisol and inflammation) and raise the “gas” (like natural hormone pulses and receptor sensitivity) for allopregnanolone’s activityrupahealth.compubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. A body and mind in balance will naturally favor healthy neurosteroid levels.
For individuals on TRT, these strategies become even more pertinent – one must be proactive in maintaining the upstream hormone levels that TRT alone might diminishexcelmale.com. Integrating approaches like hCG therapy, periodic hormone monitoring, and judicious use of precursor supplements can make a significant difference in neurosteroid balance while on testosterone therapy.
It’s heartening to note that the role of allopregnanolone in mental health is gaining recognition in mainstream medicine. The success of treatments like brexanolone and zuranolone for depression showcases that modulating neurosteroids is a viable and effective therapeutic avenuefrontiersin.org. What this means for someone seeking to help themselves is that you are focusing on a truly impactful factor for mood and anxiety. By following the guide above, you are essentially implementing your own personalized “neurosteroid therapy” in a natural, holistic way.
Finally, always coordinate with healthcare professionals when making changes, especially in the context of TRT or if you have underlying health conditions. Hormones and neurosteroids form a complex web – adjusting one piece can affect others. A doctor can help order the right tests (to avoid guessing) and ensure that any supplementation or medication is done safely. That said, many of the lifestyle and dietary recommendations are safe and beneficial for overall health, so you can certainly start with those on your own. Improvements may be gradual, but over time you may notice steadier mood, less anxiety, better sleep, and an enhanced sense of well-being as your allopregnanolone levels build up or normalize.
In summary, boosting allopregnanolone is a promising strategy for supporting mental health. By fueling your brain’s ability to “make its own calm”, you address mood and anxiety at a fundamental level. It’s a comprehensive approach – part endocrine, part lifestyle – but the reward is potentially a more balanced mood from within. With persistence and careful management, you can harness the power of this neurosteroid to improve your quality of life, even while on therapies like TRT. Here’s to achieving a better neurohormonal balance and reaping the mental health benefits that come with it!
References:
- Bali A, Jaggi AS. (2014). Multifunctional aspects of allopregnanolone in stress and related disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 48, 64-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.09.005. (Overview of allopregnanolone’s effects in stress disorders)rupahealth.com
- Pinna G et al. (2004). SSRIs act as selective brain steroidogenic stimulants (SBSSs). Brain Research Reviews, 46(2), 92-104. (Noted that fluoxetine and similar SSRIs increase brain allopregnanolone content independent of serotonin)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Marx CE, et al. (2014). Allopregnanolone elevations following pregnenolone administration are associated with enhanced activation of emotion regulation neurocircuits. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 231(17), 3581-3595. DOI: 10.1007/s00213-014-3502-y. (Demonstrated pregnenolone raises allopregnanolone ~3x in plasma and reduces anxiety circuits reactivity)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Kimball A, et al. (2020). The allopregnanolone to progesterone ratio across the menstrual cycle and in menopause. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 112, 104512. DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104512. (Discusses fluctuations of progesterone and ALLO; ALLO rises in luteal phase and drops in menopause)rupahealth.comrupahealth.com
- Ottander U, et al. (2005). Allopregnanolone and pregnanolone are produced by the human corpus luteum and their release is stimulated by hCG. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 239(1-2), 37-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2005.04.007. (Found hCG increased progesterone 2-3x and allopregnanolone ~2x in luteal cells)pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Rupa Health. Allopregnanolone Biomarker Overview. (2023). (Provides a summary of allopregnanolone’s role and natural ways to support it; notes on lifestyle, herbs, and medications like finasteride affecting ALLO)rupahealth.comrupahealth.com
- Diviccaro S, et al. (2022). Allopregnanolone: An overview on its synthesis and effects. J Neuroendocrinol, 34(2), e12996. DOI: 10.1111/jne.12996. (Recent review on how allopregnanolone is synthesized in the brain and its multifaceted effects, including GABA modulation and neuroprotection)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Locci A, Pinna G. (2019). Neurosteroids and Postpartum Depression: The Role of Allopregnanolone. Brain Sciences, 9(4), 93. DOI: 10.3390/brainsci9040093. (Discusses the drop in ALLO postpartum and the therapeutic use of brexanolone; mechanism of SSRIs raising ALLO in depression treatment)
- Pinna G. (2020). Allopregnanolone, the neuromodulator turned therapeutic agent: Thank you, next? Front Endocrinol, 11, 236. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00236. (Perspective on using allopregnanolone therapeutically in PTSD, depression; mentions ALLO deficiency in those conditions and trials of neurosteroid therapies)pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Marecki R, et al. (2023). Zuranolone – synthetic neurosteroid in treatment of mental disorders: narrative review. Front Psychiatry, 14, 1298359. DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1298359. (Summarizes current knowledge on zuranolone and other neurosteroid drugs; confirms FDA approval of zuranolone for PPD in Aug 2023 and its mechanism as GABA modulator)frontiersin.orgfrontiersin.org
- Soderpalm AH, et al. (2004). Administration of progesterone produces similar effects in men and women on indices of sedation and on plasma allopregnanolone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 29(2), 161-177. DOI: 10.1016/S0306-4530(02)00128-6. (Found that oral progesterone raised allopregnanolone and had sedative/anxiolytic effects in both men and women – evidence of progesterone’s conversion to calming neurosteroids)
- Porcu P, et al. (2016). Neurosteroids and ethanol action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 162, 94-101. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.06.002. (Explains how alcohol acutely increases brain allopregnanolone and the role of neurosteroids in alcohol’s effects, as well as the consequences of chronic use on neurosteroid levels)
- Chartoff EH, Mavrikaki M. (2015). Sex differences in kappa opioid receptor function and their potential impact on addiction. Front Neurosci, 9, 466. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00466. (Included here for context on steroidogenesis in stress; touches on pregnenolone steal concept in chronic stress)
- Vergel N. Pregnenolone for Men: What You Need to Know. (2021, DiscountedLabs.com blog).discountedlabs.comdiscountedlabs.com (Provides practical insights into pregnenolone supplementation, citing studies of pregnenolone raising allopregnanolone 3× to 5×, and discusses its effects on mood and hormone balance, especially in men on TRT).
Last edited by a moderator: