madman
Super Moderator
Nelson's house always on point here!
You know where it's at LOL!
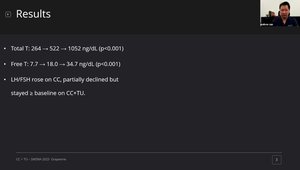
* The mean baseline total testosterone was 264 ± 61 ng/dL. After three months of CC monotherapy, mean total testosterone significantly increased to 522 ± 101 ng/dL; FSH and LH levels also rose significantly. However, patients reported minimal symptomatic improvement. Upon adding oral TU to the CC regimen for an additional three months, mean peak total testosterone levels significantly increased to 1052 ± 293 ng/dL. Notably, with combination therapy, FSH levels (mean 5.2 ± 3.7 mIU/mL) and LH levels (mean 3.5 ± 1.8 mIU/mL) remained at or above pre-treatment baseline levels, despite the significant increase in exogenous testosterone. Eighteen of 20 patients (90%) reported significantly improved symptomatic outcomes on the combined regimen. No testicular atrophy was reported during the six-month study period, and three patients on combined therapy reported spontaneous natural conception with their partners.
* The combination of clomiphene citrate and oral testosterone undecanoate demonstrated a substantial increase in total testosterone levels and provided significant symptomatic relief in men with TD who had an inadequate response to CC monotherapy. Crucially, this dual-mechanism approach appears to preserve HPG axis activity, as evidenced by maintained gonadotropin levels. These findings suggest a novel, effective, and potentially synergistic therapeutic strategy for managing TD, offering benefits over monotherapy, particularly for patients concerned with testicular function and fertility.
A Novel Combination Therapy for Testosterone Deficiency: Clomiphene Citrate With Oral Testosterone Undecanoate Provides Symptomatic Relief With Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis Preservation
Sun, A (2025)
1 - Urology Partners of North Texas
Introduction
Testosterone deficiency (TD) in men presents treatment challenges: traditional testosterone replacement therapies (TRTs) suppress endogenous production, while clomiphene citrate (CC) monotherapy, despite stimulating LH/FSH for endogenous testosterone, often yields suboptimal symptomatic relief. Attempts to combine CC with injectable TRT generally still suppress gonadotropins. Oral testosterone undecanoate (TU), with its unique lymphatic absorption and potentially less HPG axis suppression due to its short-acting nature, offers a novel agent to combine with CC, aiming to improve symptoms and testosterone levels while preserving testicular function, addressing an unmet need in TD management.
Objective
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and impact on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis of combining clomiphene citrate (CC) with oral testosterone undecanoate (TU) in men with testosterone deficiency (TD) who reported insufficient symptomatic benefit from CC monotherapy.
Methods
This retrospective chart review included 20 men, aged 23-72 years, from a high-volume community urology practice, with clinically confirmed TD (serum testosterone < 400 ng/dL and associated symptoms). Patients were initially treated with CC 50mg every other day for three months to stimulate endogenous testosterone. Following this period, patients reporting insufficient symptomatic benefit were offered oral TU (Kyzatrex) 400mg once daily as a single lunchtime dose, while continuing CC 50mg QOD, for approximately three additional months. Outcomes assessed were changes in serum total testosterone, free testosterone, LH, FSH, SHBG, estradiol, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. Patient-reported symptomatic benefit and safety was monitored through patient self-reporting.
Results
The mean baseline total testosterone was 264 ± 61 ng/dL. After three months of CC monotherapy, mean total testosterone significantly increased to 522 ± 101 ng/dL; FSH and LH levels also rose significantly. However, patients reported minimal symptomatic improvement. Upon adding oral TU to the CC regimen for an additional three months, mean peak total testosterone levels significantly increased to 1052 ± 293 ng/dL. Notably, with combination therapy, FSH levels (mean 5.2 ± 3.7 mIU/mL) and LH levels (mean 3.5 ± 1.8 mIU/mL) remained at or above pre-treatment baseline levels, despite the significant increase in exogenous testosterone. Eighteen of 20 patients (90%) reported significantly improved symptomatic outcomes on the combined regimen. No testicular atrophy was reported during the six-month study period, and three patients on combined therapy reported spontaneous natural conception with their partners. Two patients required TU dose reduction for hematocrit levels above 52%, and two reported mild, transient adverse events (nausea, headache) that resolved without intervention.
Conclusions
The combination of clomiphene citrate and oral testosterone undecanoate demonstrated a substantial increase in total testosterone levels and provided significant symptomatic relief in men with TD who had an inadequate response to CC monotherapy. Crucially, this dual-mechanism approach appears to preserve HPG axis activity, as evidenced by maintained gonadotropin levels. These findings suggest a novel, effective, and potentially synergistic therapeutic strategy for managing TD, offering benefits over monotherapy, particularly for patients concerned with testicular function and fertility. This approach warrants further investigation in larger, prospective, controlled studies.
Figure 1:

Figure 2

You know where it's at LOL!
* The mean baseline total testosterone was 264 ± 61 ng/dL. After three months of CC monotherapy, mean total testosterone significantly increased to 522 ± 101 ng/dL; FSH and LH levels also rose significantly. However, patients reported minimal symptomatic improvement. Upon adding oral TU to the CC regimen for an additional three months, mean peak total testosterone levels significantly increased to 1052 ± 293 ng/dL. Notably, with combination therapy, FSH levels (mean 5.2 ± 3.7 mIU/mL) and LH levels (mean 3.5 ± 1.8 mIU/mL) remained at or above pre-treatment baseline levels, despite the significant increase in exogenous testosterone. Eighteen of 20 patients (90%) reported significantly improved symptomatic outcomes on the combined regimen. No testicular atrophy was reported during the six-month study period, and three patients on combined therapy reported spontaneous natural conception with their partners.
* The combination of clomiphene citrate and oral testosterone undecanoate demonstrated a substantial increase in total testosterone levels and provided significant symptomatic relief in men with TD who had an inadequate response to CC monotherapy. Crucially, this dual-mechanism approach appears to preserve HPG axis activity, as evidenced by maintained gonadotropin levels. These findings suggest a novel, effective, and potentially synergistic therapeutic strategy for managing TD, offering benefits over monotherapy, particularly for patients concerned with testicular function and fertility.
A Novel Combination Therapy for Testosterone Deficiency: Clomiphene Citrate With Oral Testosterone Undecanoate Provides Symptomatic Relief With Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis Preservation
Sun, A (2025)
1 - Urology Partners of North Texas
Introduction
Testosterone deficiency (TD) in men presents treatment challenges: traditional testosterone replacement therapies (TRTs) suppress endogenous production, while clomiphene citrate (CC) monotherapy, despite stimulating LH/FSH for endogenous testosterone, often yields suboptimal symptomatic relief. Attempts to combine CC with injectable TRT generally still suppress gonadotropins. Oral testosterone undecanoate (TU), with its unique lymphatic absorption and potentially less HPG axis suppression due to its short-acting nature, offers a novel agent to combine with CC, aiming to improve symptoms and testosterone levels while preserving testicular function, addressing an unmet need in TD management.
Objective
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and impact on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis of combining clomiphene citrate (CC) with oral testosterone undecanoate (TU) in men with testosterone deficiency (TD) who reported insufficient symptomatic benefit from CC monotherapy.
Methods
This retrospective chart review included 20 men, aged 23-72 years, from a high-volume community urology practice, with clinically confirmed TD (serum testosterone < 400 ng/dL and associated symptoms). Patients were initially treated with CC 50mg every other day for three months to stimulate endogenous testosterone. Following this period, patients reporting insufficient symptomatic benefit were offered oral TU (Kyzatrex) 400mg once daily as a single lunchtime dose, while continuing CC 50mg QOD, for approximately three additional months. Outcomes assessed were changes in serum total testosterone, free testosterone, LH, FSH, SHBG, estradiol, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. Patient-reported symptomatic benefit and safety was monitored through patient self-reporting.
Results
The mean baseline total testosterone was 264 ± 61 ng/dL. After three months of CC monotherapy, mean total testosterone significantly increased to 522 ± 101 ng/dL; FSH and LH levels also rose significantly. However, patients reported minimal symptomatic improvement. Upon adding oral TU to the CC regimen for an additional three months, mean peak total testosterone levels significantly increased to 1052 ± 293 ng/dL. Notably, with combination therapy, FSH levels (mean 5.2 ± 3.7 mIU/mL) and LH levels (mean 3.5 ± 1.8 mIU/mL) remained at or above pre-treatment baseline levels, despite the significant increase in exogenous testosterone. Eighteen of 20 patients (90%) reported significantly improved symptomatic outcomes on the combined regimen. No testicular atrophy was reported during the six-month study period, and three patients on combined therapy reported spontaneous natural conception with their partners. Two patients required TU dose reduction for hematocrit levels above 52%, and two reported mild, transient adverse events (nausea, headache) that resolved without intervention.
Conclusions
The combination of clomiphene citrate and oral testosterone undecanoate demonstrated a substantial increase in total testosterone levels and provided significant symptomatic relief in men with TD who had an inadequate response to CC monotherapy. Crucially, this dual-mechanism approach appears to preserve HPG axis activity, as evidenced by maintained gonadotropin levels. These findings suggest a novel, effective, and potentially synergistic therapeutic strategy for managing TD, offering benefits over monotherapy, particularly for patients concerned with testicular function and fertility. This approach warrants further investigation in larger, prospective, controlled studies.
Figure 1:
Figure 2