Aging is one of the great universal experiences—an inevitable march that begins the moment we’re born. From the changing texture…

www.sciencenewstoday.org
What Are Telomeres and Why Do They Matter in Aging?
The Science DeskAugust 4, 2025
Aging is one of the great universal experiences—an inevitable march that begins the moment we’re born. From the changing texture of our skin to the quiet graying of hair, aging is deeply personal, yet woven into the biology of every living cell. But what if we could peel back the surface of time and look into the very machinery that drives this process? What if aging isn’t just a story written in wrinkles, but a molecular dance unfolding with every cellular division?
In recent decades, one biological player has captivated scientists and philosophers alike: the telomere. Like mysterious countdown clocks at the ends of our chromosomes, telomeres hold a key role in the story of aging, cellular health, and even mortality. Understanding telomeres is not just about slowing down wrinkles or living longer—it’s about comprehending the fundamental rules of life, death, and regeneration.
Telomeres: The Guardians at Chromosome’s End
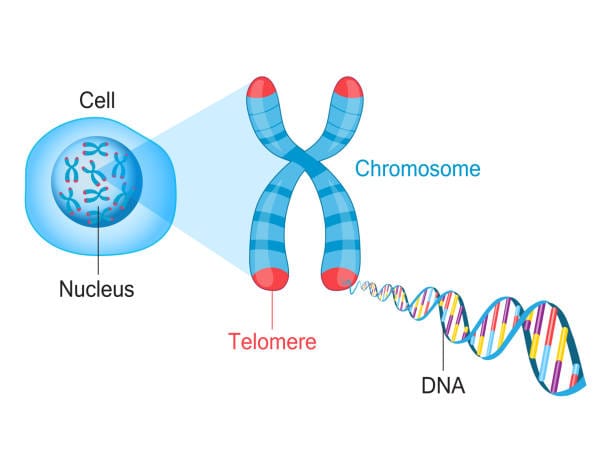
At the heart of the cell lies the nucleus, a biological vault housing our genetic blueprint—DNA. This vast code is packaged neatly into chromosomes, structures that carry instructions for everything from eye color to organ formation. But chromosomes face a peculiar problem. Every time a cell divides—a process essential for growth, healing, and maintenance—its DNA must be copied. And therein lies a dilemma.
DNA replication machinery isn’t perfect. At the very ends of each chromosome, a small segment fails to be copied. Without a buffer, vital genetic information would be lost with every division. Nature’s ingenious solution? Telomeres.
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences—imagine the code TTAGGG repeated thousands of times—capping the ends of chromosomes. These sequences don’t code for proteins; instead, they act like protective shoelace tips (aglets), preventing chromosomes from fraying, tangling, or fusing with their neighbors. Every time a cell divides, a portion of the telomere is lost rather than critical genetic information. This sacrificial protection allows the genome to remain stable through countless cycles of replication.
The Telomere Clock: Ticking Toward Cellular Aging
The telomere’s role in aging becomes clear when you realize they’re not endlessly replenished. In most somatic (body) cells, telomeres shorten with every division, slowly ticking down like biological fuses. When they reach a critically short length, cells sense danger and stop dividing. This state is called
replicative senescence—a cellular retirement that’s both protective and problematic.
Senescent cells remain metabolically active but no longer contribute to tissue growth or repair. Worse, they often secrete inflammatory molecules, growth factors, and enzymes that can damage surrounding tissues—a phenomenon known as the
senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Over time, this accumulation of “zombie” cells contributes to aging, chronic inflammation, and the degradation of tissue function.
In this way, telomere shortening acts as a biological clock, counting down the cell’s capacity to divide. And as the clock runs out, the body begins to show signs of wear: slower healing, weaker immune responses, cognitive decline, and age-related diseases.
Telomerase: The Enzyme That Rewinds the Clock
But evolution doesn’t stop at dead ends. Some cells possess a remarkable tool to restore telomeres and cheat this countdown. Enter
telomerase, a ribonucleoprotein enzyme that can rebuild telomeres by adding TTAGGG sequences back to the ends of chromosomes.
Telomerase is active in germline cells (which produce eggs and sperm), stem cells, and certain white blood cells, giving them the ability to divide extensively without losing vital genetic material. In these cells, telomerase grants a kind of cellular immortality—ensuring that humanity’s genetic code can be passed on across generations without decay.
However, in most adult somatic cells, telomerase is dormant or minimally active. This restriction serves an evolutionary purpose: it protects us from uncontrolled cell growth. Unchecked telomerase activity is a double-edged sword, because it can also enable cancer cells to bypass aging and become immortal.
Indeed, about 90% of cancers reactivate or overexpress telomerase, using it to sustain their rapid division. In this way, the same mechanism that holds promise for longevity is also a gateway to malignancy.
Telomeres and the Human Lifespan: Correlation or Causation?
Given this complex interplay, scientists have spent years exploring the relationship between telomere length and lifespan. Shorter telomeres are associated with age-related diseases—cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, osteoporosis, and even some forms of cancer. People with shorter telomeres tend to have higher mortality rates, leading some researchers to call telomere length a “biological age marker.”
But correlation is not causation. Are short telomeres merely signs of aging and disease—or do they actively drive it?
The answer lies somewhere in between. On one hand, individuals born with short telomeres due to genetic mutations (e.g., in diseases like dyskeratosis congenita) often suffer from premature aging and organ failure. On the other, artificially lengthening telomeres doesn’t always produce healthier or longer-lived organisms, and may increase cancer risk.
Still, telomere length remains a powerful predictor of biological resilience. It reflects the cumulative stress a body endures—oxidative stress, inflammation, environmental toxins, and even psychological strain can accelerate telomere erosion. In this sense, telomeres are storytellers of our lives, etched with the imprint of every hardship and healing.
Stress, Trauma, and the Invisible Aging Within
One of the most striking revelations of telomere biology is its connection to emotional well-being. Chronic psychological stress—whether from poverty, abuse, or caregiving—has been linked to accelerated telomere shortening. In groundbreaking studies, researchers like Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn and Dr. Elissa Epel found that mothers caring for chronically ill children had significantly shorter telomeres compared to mothers with healthy children.
Similarly, individuals exposed to early-life trauma, such as neglect or violence, often show signs of premature cellular aging. This suggests that the mind and body are deeply intertwined, and that emotional wounds leave molecular scars. Telomeres do not simply measure time—they measure
how we’ve lived that time.
Meditation, mindfulness, supportive relationships, and healthier lifestyles have all been shown to slow telomere loss—or, in some studies, even lengthen them. This offers a hopeful narrative: that by nourishing the mind and body, we may reclaim some control over the biology of aging.
Telomere Lengthening: The New Frontier of Anti-Aging
The tantalizing possibility of extending telomeres has spurred a wave of scientific and commercial interest. Could we slow aging—or even reverse it—by restoring telomeres?
In animal models, activating telomerase has produced promising results. Mice engineered to express telomerase lived longer and showed delayed onset of age-related diseases. In some cases, telomerase reactivation rejuvenated aged tissues, improved brain function, and enhanced regenerative capacity.
In humans, early clinical efforts are more cautious. Telomerase gene therapy has been tested in limited trials, with signs of improved health but no confirmed extension of lifespan. Some experimental compounds and natural extracts—like TA-65, astragalus root, and cycloastragenol—are marketed as telomerase activators, but the evidence remains limited and mixed.
The biggest concern is safety. Increasing telomerase activity in adult cells could risk promoting cancer. Until we fully understand how to target telomerase safely and precisely, efforts to manipulate it in aging will remain under close scrutiny.
A Cell’s Final Act: Senescence or Suicide
As telomeres shorten, cells face a critical decision: enter senescence or undergo
apoptosis, programmed cell death. Both are natural defenses against damaged or aged cells becoming dysfunctional or malignant. But an imbalance in these responses can cause trouble.
Too much senescence clogs tissues with non-dividing, inflammatory cells that impair function and healing. Too much apoptosis can lead to degenerative diseases by killing off essential cells faster than they can be replaced. Thus, telomere length acts like a traffic light—guiding the decision of whether a cell should stop, die, or persist.
Emerging anti-aging therapies now target senescent cells directly. Known as
senolytics, these compounds selectively destroy senescent cells and have shown promise in animal models, improving cardiovascular health, kidney function, and lifespan. By reducing the toxic burden of these cells, senolytics may help restore tissue vitality even as telomeres decline.
The Interplay With Mitochondria and Inflammation
Aging is not a solo performance. Telomeres interact with other key processes—mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, DNA damage—to create a symphony of decline. Shortened telomeres can trigger signals that damage mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of the cell. In turn, malfunctioning mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage DNA and accelerate telomere loss—a vicious cycle.
Inflammation, too, plays a central role. Chronic low-grade inflammation—dubbed “inflammaging”—erodes telomeres and disrupts cellular repair mechanisms. It’s a slow-burning fire that weakens the scaffolding of life, often without symptoms until disease emerges.
Understanding these interconnected pathways is crucial. It suggests that targeting telomeres alone may not be enough—we must also preserve mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative stress, and control inflammation to extend healthspan.
Telomeres in the Public Eye: Hope, Hype, and Responsibility
The popular fascination with telomeres has given rise to a booming industry of tests, supplements, and therapies. Companies offer telomere length testing to gauge your “biological age,” promising personalized insights into your health trajectory. Anti-aging clinics offer experimental treatments, often ahead of solid scientific consensus.
While telomere testing can provide interesting data, it remains an imperfect science. Telomere length varies between tissues and individuals. It changes with stress, illness, and lifestyle. A single measurement, often from blood cells, may not reflect the full complexity of your biology.
Still, the idea that we might measure and modulate our biological aging is powerful. It challenges us to see aging not as a passive decline, but as a dynamic process shaped by choices, environments, and relationships.
The Future of Aging: From Biology to Philosophy
As we peer into the molecular secrets of aging, telomeres force us to confront profound questions. If we could extend life indefinitely, should we? What does it mean to age with dignity? How do we balance cellular immortality with human mortality?
Some scientists envision a future where telomere therapies extend human healthspan dramatically. Others caution against hubris, warning that life’s richness comes not from evading death, but from finding meaning within it. The biology of telomeres may offer new tools—but how we wield them will reflect our values as much as our knowledge.
In the meantime, telomere research continues to unveil the subtle, beautiful logic of life. Each cell division, each shortening telomere, is a reminder that life is both fragile and resilient. And in the dance of aging, there is still much to learn—and much to celebrate.