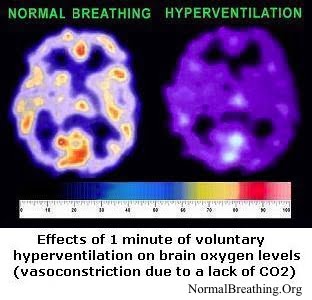
The ancient medical techniques of fasting and breath control are finally getting the attention they deserve. Here is a paper on the physiological effects of breath control.
Key points
Key points
- Slow breathing practices have gained popularity in the western world due to their claimed health benefits, yet remain relatively untouched by the medical community.
- Investigations into the physiological effects of slow breathing have uncovered significant effects on the respiratory, cardiovascular, cardiorespiratory and autonomic nervous systems.
- Key findings include effects on respiratory muscle activity, ventilation efficiency, chemoreflex and baroreflex sensitivity, heart rate variability, blood flow dynamics, respiratory sinus arrhythmia, cardiorespiratory coupling, and sympathovagal balance.
- There appears to be potential for use of controlled slow breathing techniques as a means of optimising physiological parameters that appear to be associated with health and longevity, and that may extend to disease states; however, there is a dire need for further research into the area.