Nelson Vergel
Founder, ExcelMale.com
J Appl Res. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 Mar 3.
Published in final edited form as:
J Appl Res. 2009 Jan 1; 9(4): 159–165.
Clinical Experience of a Diet Designed to Reduce Aging
Ron Rosedale, M.D., Eric C. Westman, M.D., M.H.S.,1 and John P. Konhilas, Ph.D.
Abstract
Objective:
Aging is associated with elevated levels of glucose, insulin, and triglycerides. Our objective was to assess the effect of a nutritional program designed to reduce these correlates of aging.
Design:
This is a retrospective chart review of patients attending an outpatient metabolic management program including a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet, nutritional supplementation and periodic individual visits. Outcomes measured at baseline and follow-up included body weight, fasting serum glucose, insulin, leptin, lipids, and thyroid hormone.
Results:
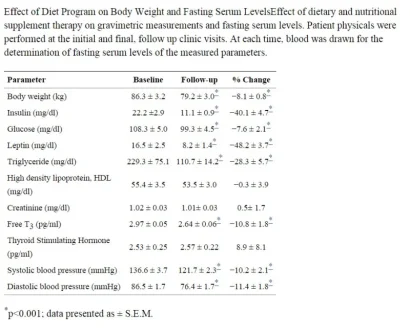
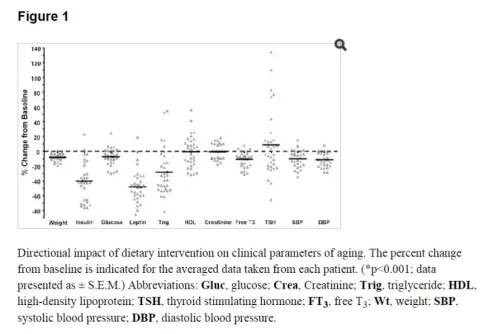
Thirty-one patients were identified with complete information. The mean age of patients was 57.6 ± 2.4 consisting of 53% female and 47% male patients. The average duration between follow up visits was 91.5 ± 8.5 days. Of the parameters measured at the follow-up visit, body weight, serum leptin, insulin, fasting glucose, triglyceride, and free T3 significantly decreased by 8.1 ± 0.8%, 48.2 ± 3.8%, 40.1 ± 4.7%, 7.6 ± 2.1%, 28.3 ± 5.7%, and 10.8 ± 1.8%, respectively. Furthermore, the triglyceride/high density lipoprotein ratio decreased from 5.1 ± 1.7 to 2.6 ± 0.5.
Conclusions:
In the context of an outpatient medical clinic, a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet with nutritional supplementation led to improvements in serum factors related to the aging process. Further research regarding this dietary approach and its relationship to aging is in order.


Published in final edited form as:
J Appl Res. 2009 Jan 1; 9(4): 159–165.
Clinical Experience of a Diet Designed to Reduce Aging
Ron Rosedale, M.D., Eric C. Westman, M.D., M.H.S.,1 and John P. Konhilas, Ph.D.
Abstract
Objective:
Aging is associated with elevated levels of glucose, insulin, and triglycerides. Our objective was to assess the effect of a nutritional program designed to reduce these correlates of aging.
Design:
This is a retrospective chart review of patients attending an outpatient metabolic management program including a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet, nutritional supplementation and periodic individual visits. Outcomes measured at baseline and follow-up included body weight, fasting serum glucose, insulin, leptin, lipids, and thyroid hormone.
Results:
Thirty-one patients were identified with complete information. The mean age of patients was 57.6 ± 2.4 consisting of 53% female and 47% male patients. The average duration between follow up visits was 91.5 ± 8.5 days. Of the parameters measured at the follow-up visit, body weight, serum leptin, insulin, fasting glucose, triglyceride, and free T3 significantly decreased by 8.1 ± 0.8%, 48.2 ± 3.8%, 40.1 ± 4.7%, 7.6 ± 2.1%, 28.3 ± 5.7%, and 10.8 ± 1.8%, respectively. Furthermore, the triglyceride/high density lipoprotein ratio decreased from 5.1 ± 1.7 to 2.6 ± 0.5.
Conclusions:
In the context of an outpatient medical clinic, a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet with nutritional supplementation led to improvements in serum factors related to the aging process. Further research regarding this dietary approach and its relationship to aging is in order.